Hemorrhoids
Rectal Procedures
- Fistulotomy
- Hemorrhoid band ligation
- Hemorrhoidectomy (Excision of external hemorrhoids)
- Pilonidal Cyst Excision
- Sphincterotomy
 |
| Click Image to Enlarge |
What are hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are veins, normally present in and around the anus and lower rectum, that have become swollen due to stretching under pressure. These are very common in both men and women, and about half the population have hemorrhoids by age 50. Hemorrhoids are also common in pregnant women due to the pressure of the fetus in the abdomen, as well as hormonal changes, which cause hemorrhoidal vessels to enlarge. The process of childbirth also puts severe stress of these vessels.
Hemorrhoids are either internal (inside the anus) or external (under the skin around the anus).
What causes hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids may develop as a result of repeated straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, heredity, aging, and chronic constipation or diarrhea.
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
The following are the most common symptoms of hemorrhoids. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
-
Bright red blood present on the stool, toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl
-
Irritation and pain around the anus
-
Swelling or a hard lump around the anus
-
Itching
The symptoms of hemorrhoids may resemble other medical conditions or problems. Always consult your doctor for a diagnosis.
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
The presence of blood in the stool can be indicative of other digestive disorders, including colorectal cancer, so thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis is important.
Diagnosing hemorrhoids may include:
-
Physical examination. This is done to check the anus and rectum and look for swollen blood vessels that indicate hemorrhoids.
-
Digital rectum examination (DRE). The doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to check for abnormalities.
-
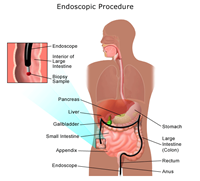
Anoscopy. A hollow, lighted tube useful for viewing internal hemorrhoids is inserted into the anus.
-
Proctoscopy. A lighted tube, which allows the doctor to completely examine the entire rectum, is inserted into the anus.
-
Sigmoidoscopy. A diagnostic procedure that allows the doctor to examine the inside of a portion of the large intestine, and is helpful in identifying the causes of diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, abnormal growths, and bleeding. A short, flexible, lighted tube, called a sigmoidoscope, is inserted into the intestine through the rectum. The scope blows air into the intestine to inflate it and make viewing the inside easier.
-
Colonoscopy. A procedure that allows the doctor to view the entire length of the large intestine, and can often help identify abnormal growths, inflamed tissue, ulcers, and bleeding. It involves inserting a colonoscope, a long, flexible, lighted tube, in through the rectum up into the colon. The colonoscope allows the doctor to see the lining of the colon, remove tissue for further examination, and possibly treat some problems that are discovered.
 |
Treatment for hemorrhoids
Specific treatment for hemorrhoids will be determined by your doctor, based on:
-
Your age, overall health, and medical history
-
Extent of the condition
-
Your tolerance of specific medicines, procedures, or therapies
-
Expectations for the course of the condition
-
Your opinion or preference
Medical treatment of hemorrhoids is aimed at relieving symptoms and may include the following:
-
Sitting in plain, warm water in the tub several times a day
-
Ice packs to reduce swelling
-
Application of hemorrhoidal creams or suppositories
Your physician may also recommend increasing both fiber and fluids to soften stools. A softer stool lessens pressure on hemorrhoids caused by straining. Good sources of fiber include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Bulk stool softeners or fiber supplements, such as psyllium (Metamucil) or methylcellulose (Citrucel), may also be recommended.
In some cases, it is necessary to treat hemorrhoids surgically. Several surgical techniques are used to remove or reduce internal and external hemorrhoids. These include the following:
-
Rubber band ligation. A rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid inside the rectum to cut off circulation to the hemorrhoid. The hemorrhoid then gradually shrinks and withers away within a few days.
-
Sclerotherapy. A chemical solution is injected around the blood vessel to shrink the hemorrhoid.
-
Electrical or laser coagulation or infrared photo coagulation. Techniques that use special devices to burn hemorrhoidal tissue.
-
Hemorrhoidectomy. A surgical procedure that permanently removes the hemorrhoids.